Osteochondrosis is a chronically occurring pathological process in which the vertebrae and the intervertebral discs located between them undergo degenerative-dystrophic changes. Most often, this disease affects the cervical and lumbar spine. The thoracic spine is affected much less frequently, but this pathology presents certain difficulties in terms of differential diagnosis, as it can be confused with cardiac, pulmonary, or any other diseases. In this article, we will look at thoracic osteochondrosis in terms of symptoms and treatment.
Clinical picture in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
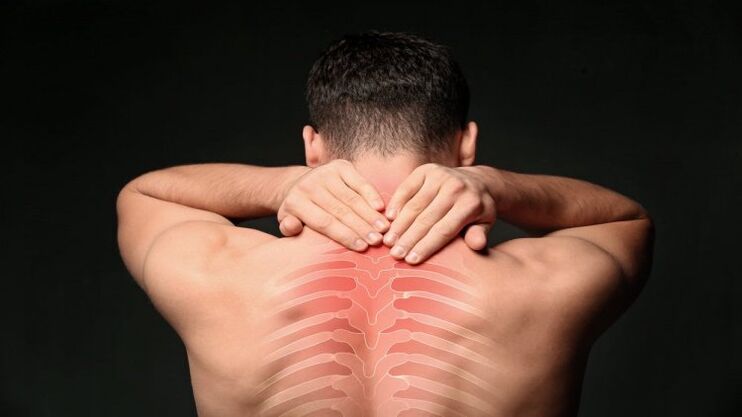
The leading clinical sign of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the thoracic spine is pain syndrome localized between the shoulder blades, in the chest, along the ribs, and so on.
Some patients report moderate pain, others report extremely severe pain. The pain syndrome is aggravated by taking a deep breath, turning or tilting the torso, raising the arms, as well as other types of physical activity. Due to the localization of pain, osteochondrosis can be confused with angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, pancreatitis, and some other diseases. It is extremely important to conduct a thorough differential diagnosis.
Due to severe pain, the patient cannot take a deep breath, which causes him to feel short of breath. In parallel, sensitive disorders of the upper extremities are often observed in the form of their numbness, tingling and much more, muscle tension in the back. In some cases, the clinical picture is supplemented by disorders in the digestive system, for example, bloating, epigastric pain, heartburn, and so on.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
First of all, during the period of exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, it is recommended to adhere to bed or at least half-bed rest.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain.
In 2014, scientists from the Kazakh National Medical University published a paper, the results of which established the effectiveness of complex treatment of osteochondrosis with the use of muscle relaxants.
As for muscle relaxants, they are aimed at stopping muscle spasm.
The treatment plan is necessarily supplemented with B vitamins, physiotherapy procedures. Of the physiotherapeutic methods, electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, phonophoresis, and so on can be used.
After stopping the acute process, the patient may be prescribed courses of massage, therapeutic exercises.
In some cases, the issue of surgical intervention may be decided, for example, in the presence of an intervertebral hernia that compresses the spinal cord.























